Source – SV Verification Directory
Packed and Unpacked Array
Packed and unpacked arrays are differentiated based on the way the arrays are stored in the memory. Generally, simulators store each element on a 32-bit word boundary. In a packed array, the elements are stored in contiguous memory locations whereas in an unpacked array, the elements are not stored in contiguous memory locations.
Packed Array
A packed array can be declared by declaring the dimension before the identifier name shown below:
logic [3:0][7:0] arr_packed;
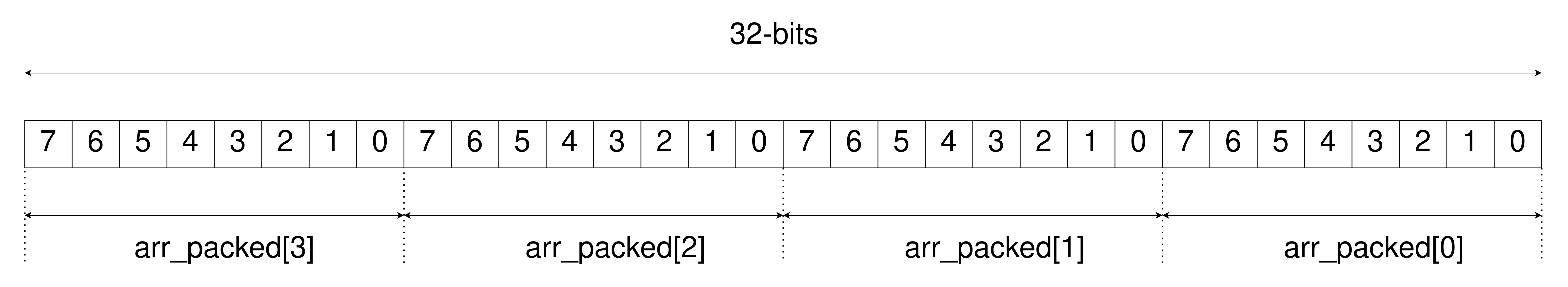
Figure 1: Packed Array
Unpacked Array
An unpacked array is declared when the identifier name is in between the dimensions of the array as shown below:
logic [3:0] arr_unpacked [3];
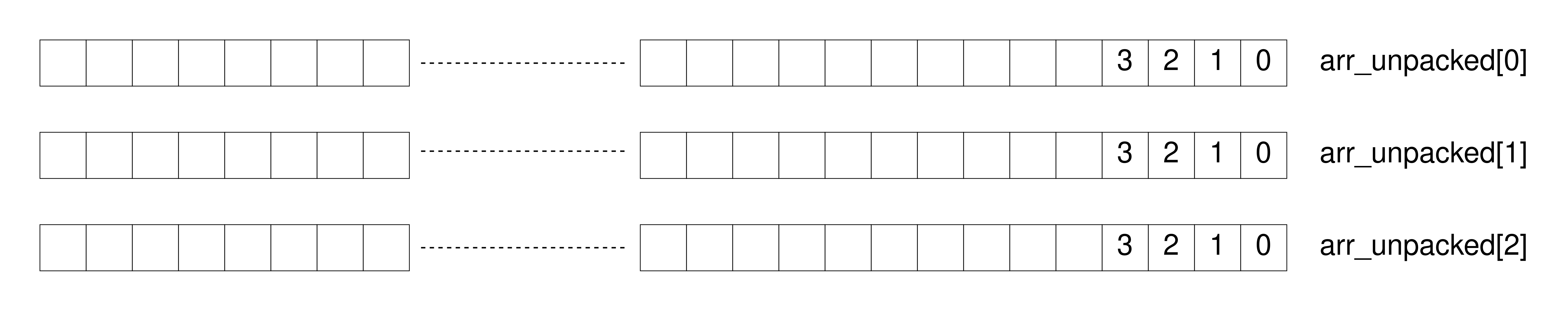
Figure 2: Unpacked Array
Mixed arrays, consisting of packed/unpacked arrays can be declared. When reading a value from an array always read from left to right, eg. array [1st position] [2nd position] [3rd position].
- 1st position: indicates the complete 32-bit array location in memory.
- 2nd position: indicates the byte/8-bits from the 32-bit array.
- 3rd position: indicates the bit location in the array.
To access a bit all the positions must be declared, to access a byte of memory from the array 1st and 2nd positions must be declared, and to access the complete 32-bit of the memory location only the 1st position can be declared.
Choosing Between Packed and Unpacked Arrays
Packed Array
- When modeling data types that directly map to hardware, such as vectors, signals, and registers.
- When accessing memory as a byte, a word, or a bit.
- When a change in an array occurs at “@”. This is only legal with scalar values and packed arrays.
Unpacked Array
- When you need to model multi-dimensional arrays or complex types like structs and classes, etc.
- Accessing elements is straightforward. Flexibility to access words, bytes, or bits is not required.
Packed and Unpacked array initialization and manipulation are shown below:
module packed_and_unpacked ();
logic [3:0][7:0] arr_packed;
logic [3:0] arr_unpacked [4];
initial begin
arr_packed = '{8'h87, 8'h65, 8'h43,8'h21};
arr_unpacked = '{4'h1, 4'h2, 4'h3, 4'h4};
$display("-------------- packed Array --------------");
foreach(arr_packed[i]) $display("arr_packed[%0d] = %0h", i, arr_packed[i]);
$display("-------------- Unpacked Array --------------");
foreach(arr_unpacked[i]) $display("arr_unpacked[%0d] = %0d", i, arr_unpacked[i]);
end
endmodule